Successful gardeners know the critical role sunlight plays in the health and productivity of their plants, but do you?
You can give plants all the water and nutrients they need, but they’ll never survive without the right amount of sunlight.

Reading this guide to sunlight for your plants can help you by explaining why plants need sunlight, the difference between sunlight and artificial light, and how direct and indirect sunlight plays a role in plant development.
You can turn struggling plants around with proper light, so read on to learn more!
Why Do Plants Need Sunlight?
The problem many people who fail to have a “green thumb” share is not understanding that sunlight requirements vary with different types of plants, whether they live indoors or outdoors.
Plants require sunlight for photosynthesis, creating food for the plant to survive and grow.
To help explain how photosynthesis works, think of plant leaves as tiny solar panels capturing the sun’s radiation.
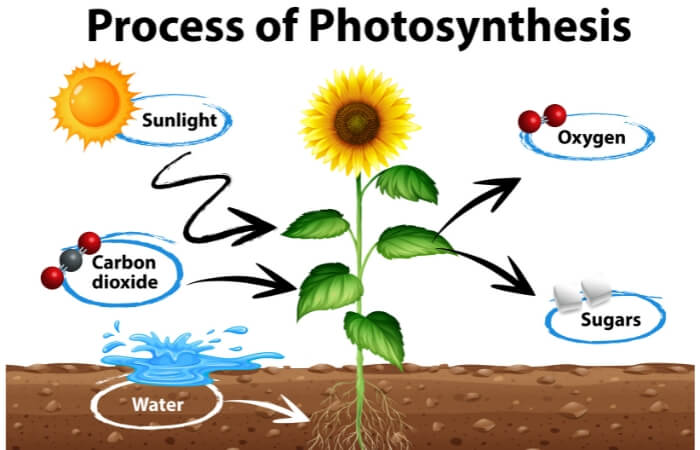
Inside a plant’s cells are chloroplasts, and inside this unit is chlorophyll which takes on the work of converting sunlight energy into organic chemicals the plant can use as food to sustain growth.
The light energy converts into two forms: ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate hydrogen).
In simple terms, ATP molecules give cells a steady supply of energy to work. At the same time, NADPH turns carbon dioxide into high-energy sugar the plant cells use to create organic molecules like glucose.
Without sunlight and the photosynthesis process, plants will starve to death because they won’t be able to make useable food that allows their cells to function.
For houseplants, placing pots in windows or sunny locations is the only way for them to receive natural light for photosynthesis. However, you can use artificial light to mimic the sun’s energy and trigger photosynthesis for plants not near a natural sunlight source.
Do Plants Need Direct Sunlight Or Just Light?
Some plants need direct sunlight for six or eight hours a day for optimal growth, while others do better with much less. Other plants do best in partial or full-shade with low sunlight exposure.
All outdoor plants will survive on direct or indirect sunlight as long as they also get the water and carbon dioxide they need.
For indoor plants, the subject of light vs. sunlight is more of an issue. Natural sunlight is always best for houseplants, whether direct or indirect.
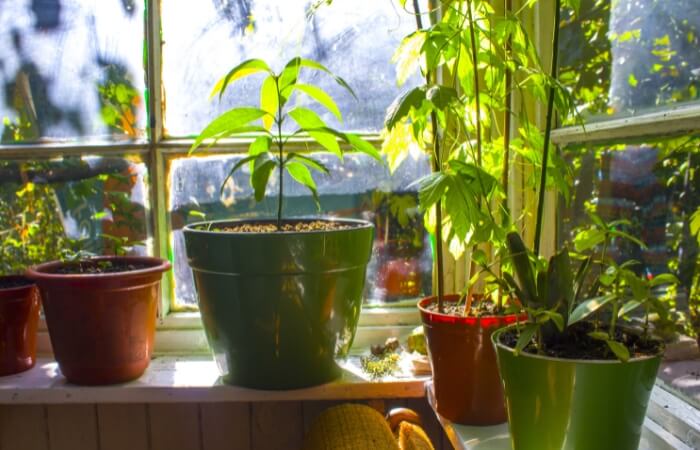

But for houseplants away from windows, the type of light it receives from lamps or other light fixtures will determine how well the plant uses it for photosynthesis.
A standard LED, or incandescent lightbulb, provides the blue, green, and red wavelengths plants utilize for photosynthesis, but the intensity ratio may not allow normal development.
If a bulb emits more red lightwaves, plants will grow more leggy than normal, with fewer leaves, but it also triggers more flowers to form.
A bulb that emits more blue lightwaves will cause plants to form thick leaves and a more compact shape.
All plants use green lightwaves for photosynthesis and reflect the excess they don’t need, which is why leaves are green.
The best thing to do for indoor plants that need artificial light is to buy special grow lights that provide the correct spectrum and intensity of lightwaves for plants to flourish.
Indirect vs Direct Sunlight
For plants, the difference between indirect and direct sunlight can mean having healthy plants or those that wilt, turn brown, have burn spots, or die.
Indirect Sunlight
Indirect sunlight is light that has to travel through a medium, such as glass, tree leaves, or a sheer curtain before it reaches the plant. Indirect light can also be sunlight reflected off another surface, such as water or metal.
Most houseplants grow best with indirect light, so they are ideal for indoor gardening. However, even houseplants vary in how much indirect light they need to receive each day.
For example, most orchids love the bright indirect light on a windowsill, but ferns prefer the less intense light away from windows.
Direct Sunlight
Direct sunlight occurs outdoors when there is no buffer between the sun’s rays and a plant.
Direct sunlight is very intense, especially during the summer when daylight hours are the longest. Many plants, especially vegetables and fruits, do best in full direct sunlight for six or more hours each day, as long as they receive sufficient water.
However, many other plants prefer partial direct sunlight, which means that the plant is in full sun during part of the day with indirect light exposure for the remaining hours.
The number of trees or structures on your property will determine what areas get full direct sun all day versus areas that receive partial direct sunlight.
What Happens If You Continue To Increase The Intensity Of Light That A Plant Receives?
If you’ve ever moved a plant that was doing well to a new location with different light exposure, you may notice changes in growth or health in only a few days.
The changes may be positive or negative, depending on how much light that particular plant species needs to produce enough energy to grow to its full potential without overdoing it.
Any increase in light intensity will boost the photosynthesis rate of a plant because it’s getting more energy from the sun on the foliage.
However, suppose the plant is not receiving enough water or carbon dioxide. In that case, photosynthesis will not increase as it needs all three to create the chemical reaction that turns the light energy into sugar.
While having more energy to grow seems beneficial to a plant, the act of photosynthesis can only happen up to a certain threshold before other reactions begin to occur inside the plant that can cause damage.
For example, once all the chlorophyll molecules available in a plant have absorbed the sun’s radiation, the intensity of the sunlight will start burning the foliage, damage cell structures, and reduce the plant’s ability to photosynthesize.
Can Full Sun Plants Grow In Shade?
Yes, most full sun plants can grow in the shade, but they’ll struggle to survive without enough energy from photosynthesis.
Plants that need full sun will begin to grow fewer leaves and produce fewer blooms. As they struggle to live, they become prone to diseases or pests that can end up killing the plant.
What Direction Gets The Most Sun Exposure?
In the US, which is in the Northern Hemisphere, the direction that receives the most sun exposure is the south. As the sun travels in the sky from east to west, it also passes to the south during every season, but light intensity is strongest in the summer.
The sun’s path means that any outdoor plants that need full sun should be on the south side of the house or far away from trees, bushes, or structures that cast shadows.
Full Partial Sun And Shade FAQs
What Is Full Sun?
In most USDA planting zones, full sun means your plant will need a minimum of six hours of direct sun exposure from late morning through late afternoon to grow well. Be aware that in far northern regions, where the sunlight is weaker, a full-sun note on the packaging will mean your plants will need a minimum of eight hours of direct sunlight each day.
What Is Partial Sun?
Partial sun means plants will need between three to six hours of direct sun per day. Ideally, this sun is around midday.
What Is Full Shade?
Full shade is a rarity to see on a seed or plant label since it means these plants require less than three hours of direct sun each day to remain healthy. Many full-shade plants can tolerate a short amount of direct sunlight in the morning or evening.
What Is Partial Shade?
Partial shade on a label means plants still require three to six hours of sun per day but should avoid the most intense mid-day sun. Many gardeners don’t have the space to avoid large trees or other objects that may impede sunlight for many hours of the day. Dappled sunlight coming through the leaves of trees is considered partial shade.
In Summary
Sunlight for your plants is just as crucial as water, so it’s essential to read plant labels or research how many hours of direct or indirect light each of your plants requires.
I hope this sunlight guide helps you better understand how plants react to light, and you use the information to give them the amount they need to thrive.
If you have struggling plants, remember that a few changes in light exposure can make a world of difference in the appearance, health, and productivity of your indoor and outdoor plants!










